Plastic injection molding stands as a cornerstone in modern manufacturing, offering efficiency, precision, and versatility. The process involves melting plastic pellets, injecting them into meticulously crafted molds, and producing durable and intricate components. Despite initial mold creation expenses, plastic injection molding emerges as a cost-effective solution for large-scale production. This article delves into the intricacies of plastic injection molding, its working principles, advantages, and a comparative analysis with 3D printing.
Plastic injection molding is a highly versatile and efficient manufacturing process used to produce a diverse array of plastic components. The method involves melting plastic pellets in an injection molding machine, then injecting the molten material into a precisely crafted mold. The mold determines the final shape of the product, and the high pressure ensures that the plastic fills the mold completely. After injection, the material cools and solidifies within the mold, taking on its intended form. The mold then opens, and the newly formed product is ejected. This process is characterized by its speed, repeatability, and ability to produce complex and detailed parts with consistent quality. Despite the initial expenses associated with mold creation, plastic injection molding is cost-effective for large-scale production due to its efficiency and the durability of the resulting products across various industries.
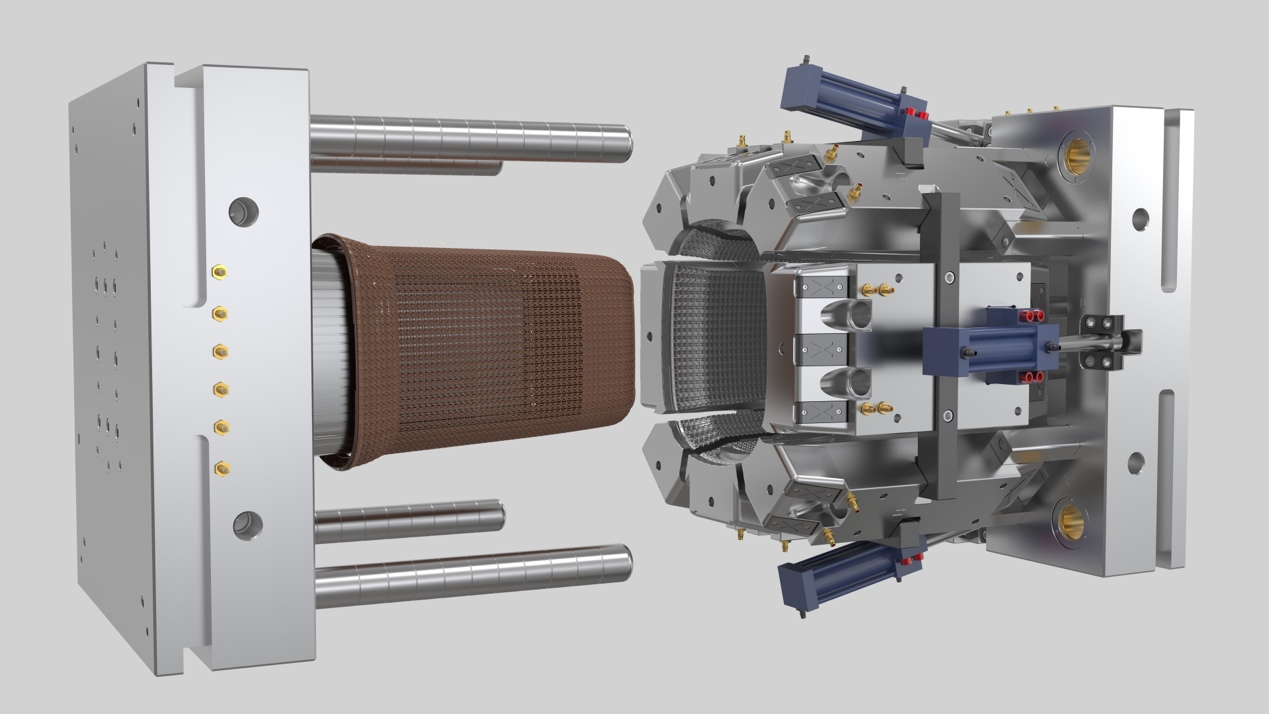
Plastic injection molding works by melting plastic pellets and injecting the molten material into a mold to create a specific shape. The process involves several key steps:
Mold Creation: A mold is designed to represent the final shape of the plastic product. Typically, the mold consists of two halves, the core, and the cavity, and is usually made of metal.
Material Preparation: Plastic pellets, usually made of polymers like polyethylene or polypropylene, are fed into the injection molding machine's hopper. The pellets are then heated until they melt and form a viscous, molten substance.
Injection: The molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. This pressure ensures that the plastic material fills the entire mold and takes on the precise shape of the mold's interior.
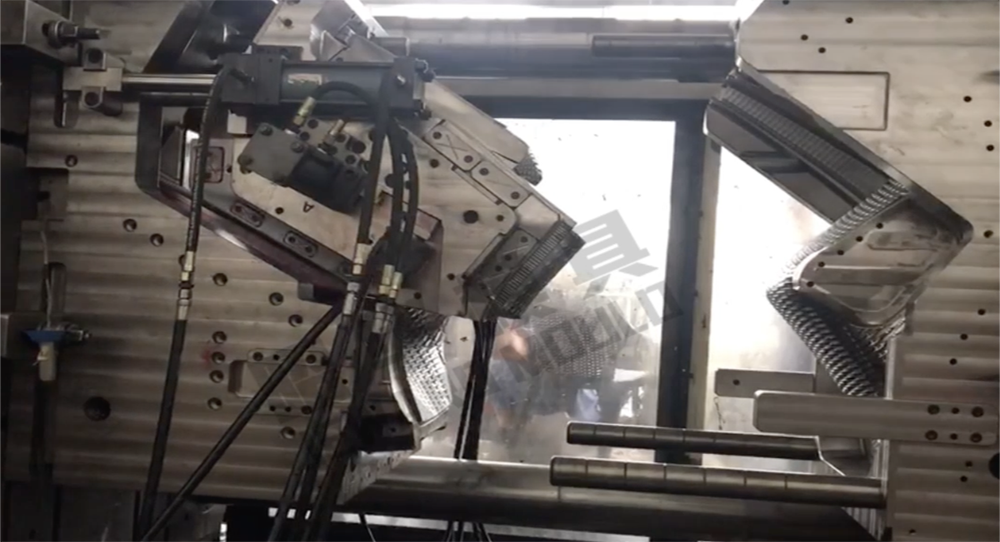
Cooling: Once injected, the molten plastic in the mold is allowed to cool and solidify. The cooling time is critical for achieving the desired properties and dimensions of the final product.
Ejection: After the plastic has solidified, the mold opens, and the newly formed plastic part is ejected using ejector pins or other mechanisms.
Quality Control: The produced parts may undergo inspection and testing to ensure they meet specified criteria. This can include visual inspection, measurements, and other quality checks.
Repeat: The entire process is repeated for the production of additional parts. Modern injection molding machines can operate with high efficiency, allowing for the mass production of identical plastic components.

Plastic injection molding offers numerous advantages that contribute to its widespread use in manufacturing. Firstly, it enables the production of intricate and complex shapes with high precision, ensuring consistent product quality. The process is highly efficient, allowing for rapid production rates and large quantities of identical items. Additionally, the ability to use a wide range of plastic materials enhances versatility, accommodating diverse product requirements. The resulting parts exhibit excellent strength and durability, often requiring minimal post-production finishing. With minimal waste generation and the potential for automation, plastic injection molding is a cost-effective solution for large-scale production. Moreover, the longevity and resilience of the molds contribute to economic feasibility over extended production runs. Overall, the combination of speed, precision, material variety, and cost-effectiveness makes plastic injection molding a preferred choice for industries seeking efficient and reliable mass production of plastic components.
Plastic Injection Molding and 3D Printing are two prominent manufacturing processes that cater to different needs within the production landscape. Plastic Injection Molding excels in mass production, leveraging molds and high-pressure injection for efficiency and precision. On the other hand, 3D Printing, renowned for its versatility, constructs objects layer by layer from digital models, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and customization. Here are six key points to explain the differences between Plastic Injection Molding and 3D Printing:
Production Method: Plastic injection molding utilizes molds and high-pressure injection for mass production with high precision. 3D printing constructs objects layer by layer from digital models, suitable for customized and prototyped items, albeit at generally slower production rates.
Materials and Properties: Plastic injection molding offers diverse material options, including high-performance plastics, yielding durable and strong products. While 3D Printing limits material choices with varying properties, ideal for prototyping but may have lower strength compared to certain molded plastics.
Speed and Scalability: Plastic injection molding is good for high-speed production and scalable for large quantities simultaneously. On the other hand, 3D printing is generally slower, more suited for small-scale production or prototyping, with limited scalability.
Tooling and Setup Costs: Plastic injection molding requires substantial tooling costs for mold creation, but unit costs decrease with larger production runs. While 3D printing makes lower tooling costs, letting it cost-effective for smaller batches, prototypes, and customized production.
Precision and Post-Processing: Plastic Injection Molding achieves high precision and detailed parts with minimal post-processing. However, 3D Printing Offers good detail but may have limitations in precision; post-processing, such as smoothing, may be necessary for certain applications.
Prototyping and Customization: Plastic Injection Molding is less suitable for rapid prototyping due to longer setup times but excels in mass production. While 3D Printing is excellent for rapid prototyping, customization, and iterative design processes, providing quick turnaround times for unique or small-batch production.
| Aspect | Plastic Injection Molding | 3D Printing |
| Production Method | Molds and high-pressure injection for mass production with high precision. | Layer-by-layer construction from digital models, suitable for customized and prototyped items, with generally slower production rates. |
| Materials and Properties | Diverse material options, including high-performance plastics, yielding durable and strong products. | Limited material choices with varying properties, suitable for prototyping but may have lower strength compared to certain molded plastics. |
| Speed and Scalability | Good for high-speed production and scalable for large quantities. | Generally slower, more suited for small-scale production or prototyping, with limited scalability. |
| Tooling and Setup Costs | Substantial tooling costs for mold creation; unit costs decrease with larger production runs. | Lower tooling costs, making it cost-effective for smaller batches, prototypes, and customized production. |
| Precision and Post-Processing | High precision and detailed parts with minimal post-processing. | Good detail but may have limitations in precision; post-processing, such as smoothing, may be necessary for certain applications. |
| Prototyping and Customization | Less suitable for rapid prototyping due to longer setup times; excels in mass production. | Excellent for rapid prototyping, customization, and iterative design processes, providing quick turnaround times for unique or small-batch production. |
In conclusion, plastic injection molding stands out as a manufacturing powerhouse, providing efficient solutions for mass production with high precision. Its advantages, including diverse material options and minimal post-processing, contribute to its widespread use in various industries. Moreover, the comparison with 3D printing highlights the nuanced strengths and trade-offs between these manufacturing methods, emphasizing the importance of selecting the right approach based on specific project requirements. As industries continue to evolve, the role of plastic injection molding remains pivotal in shaping the landscape of efficient and reliable mass production of plastic components.
